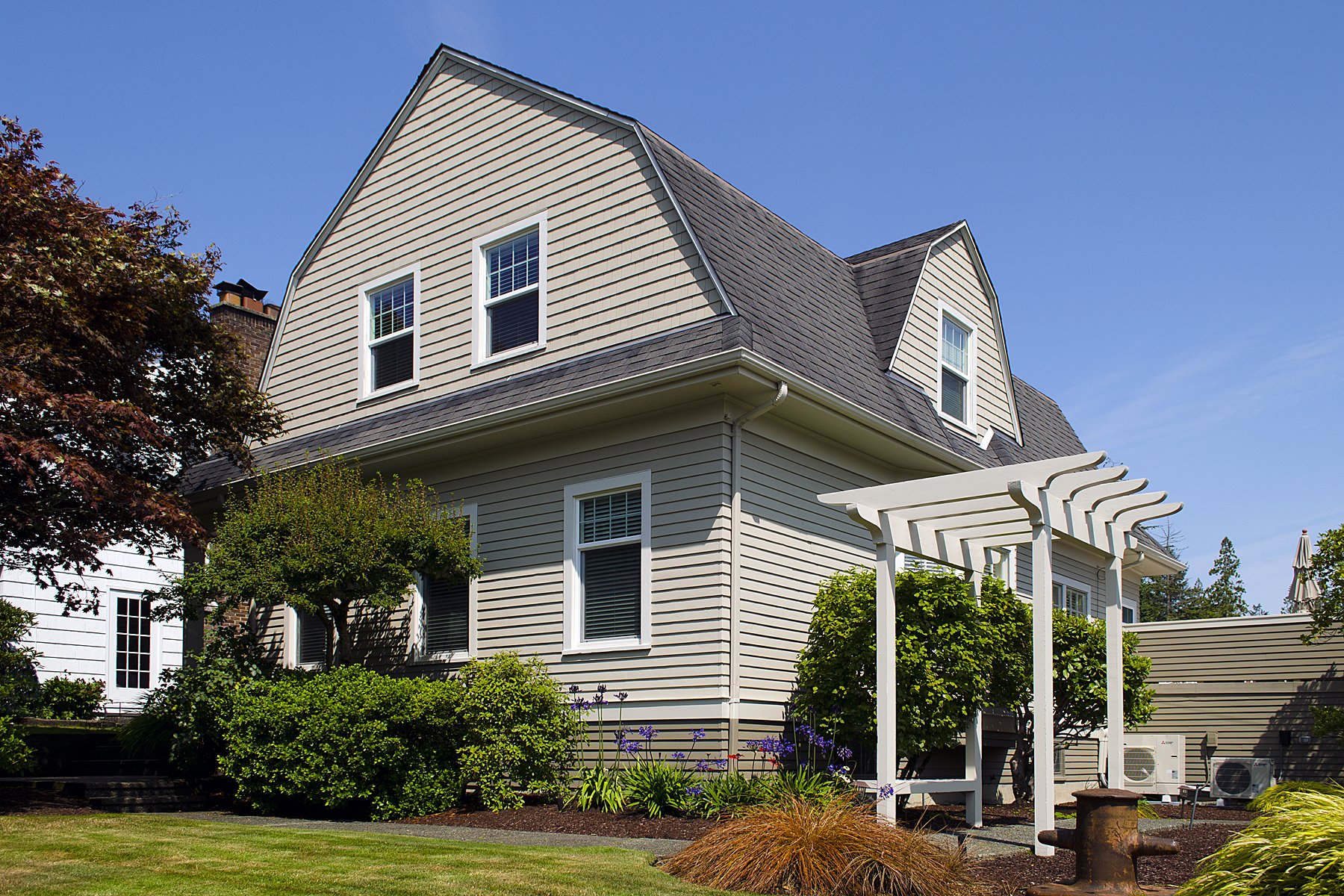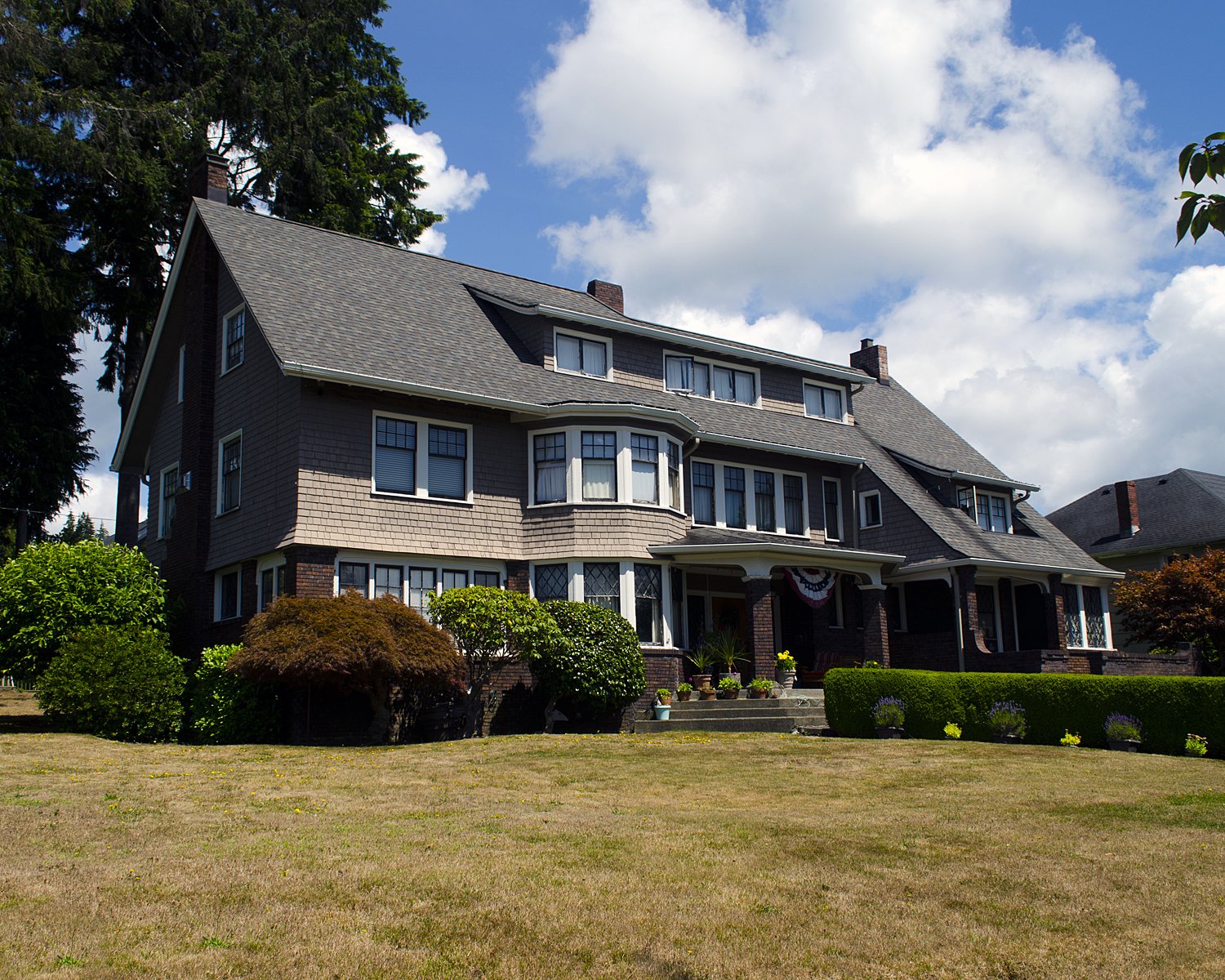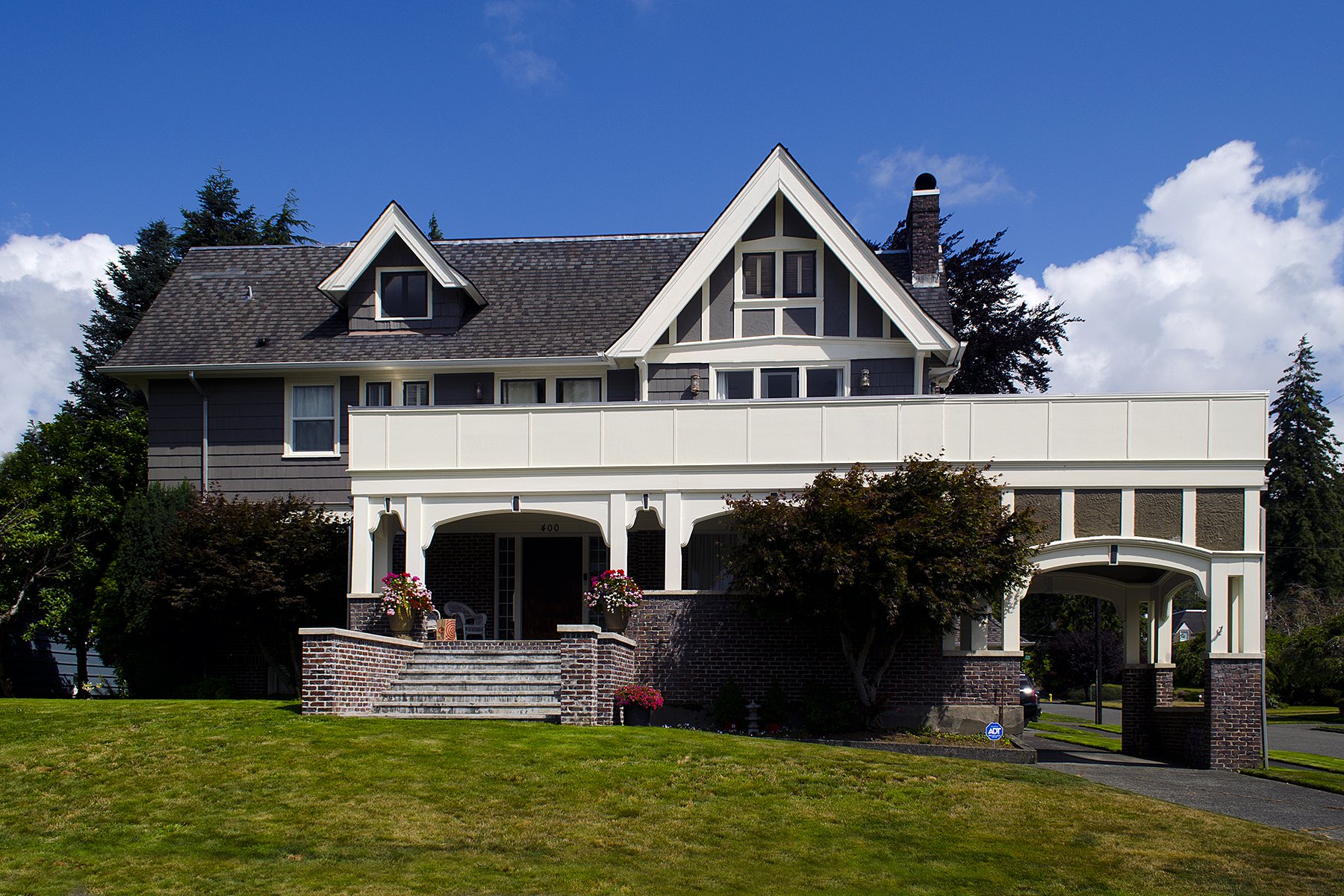
Colonial Revival
1880-1960. The Colonial Revival style took certain design elements: front façade symmetry, entrance fanlights and sidelights, pedimented doorways with porches and dormers and applied them to larger-scaled buildings. (1)

Craftsman
1890-1930. Inspired by the Arts and Crafts movement as a reaction to the Victorian "over-decorated" aesthetic. American Craftsman style incorporated a visibly sturdy structure of clean lines and natural materials.(2)

Dutch Colonial
Early 20th century. Dutch Colonial style is characterized by a gambrel roof with curved eaves along the length of the house. Modern versions are referred to as "Dutch Colonial Revival", a subtype of the Colonial Revival style. (4)
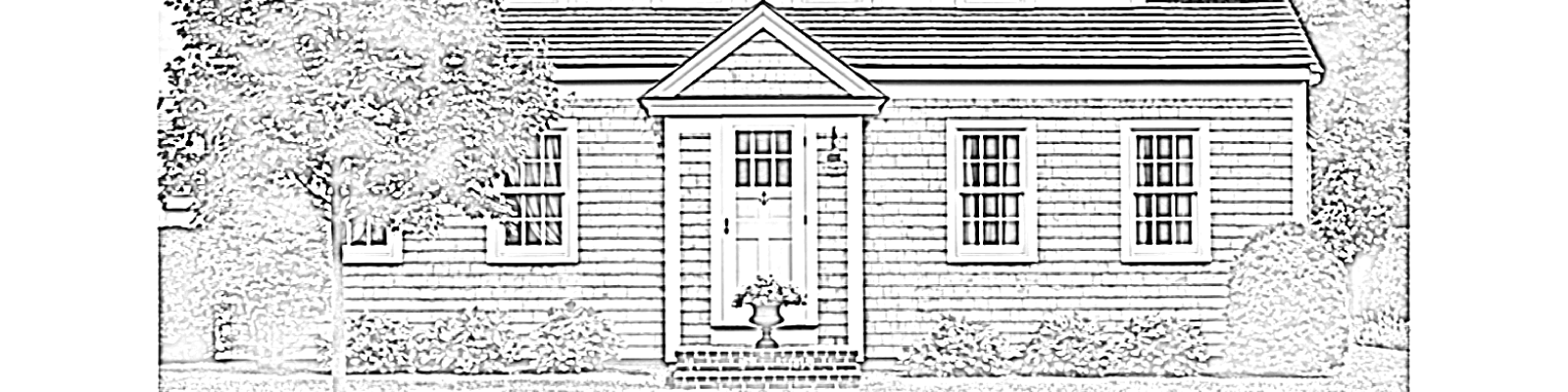

Eastern Brick and Shingle
1870-1910. Eastern Brick and Shingle consists of building exteriors covered with shingles [or brick] of a single color. The goal is to create an unembellished, uniform surface, mono-toned and unornamented. These homes celebrated the honesty of form, the purity of line. (5)

Federal Revival
1780-1830. American Federal architecture typically uses plain surfaces with attenuated detail, usually isolated in panels, tablets, and friezes. It also had a flatter, smoother façade and rarely used pilasters. (6)
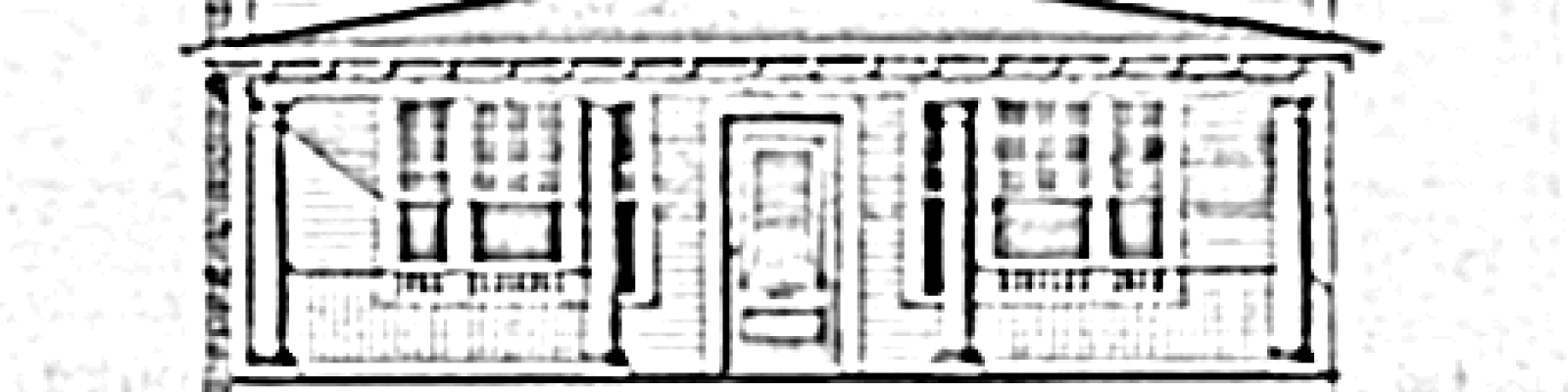
Four Square
1890-1930. The hallmarks of the style include a basically square, boxy design, two-and-one-half stories high, usually with four large, boxy rooms to a floor, a center dormer, and a large front porch with wide stairs. (7)

French Revival
1915-1945 Characteristics include a tall, steeply pitched, hipped roof with narrow eaves, often with a flare and no forward-facing gable, a masonry exterior with arched, circular, or hipped dormers. (8)

Greek Revival
1820-1850. Greek Revival style homes were usually painted white with a temple-style façade and bold round, square or even octagonal columns, gently sloping roofs with gable fronts, and elaborate door surrounds. (9)

Mid-Century Modern
1945-1970. Mid-century Modern homes are noticeable for their clean lines and geometric shapes, floor to ceiling windows, changes in elevation, and minimal decoration. (10)
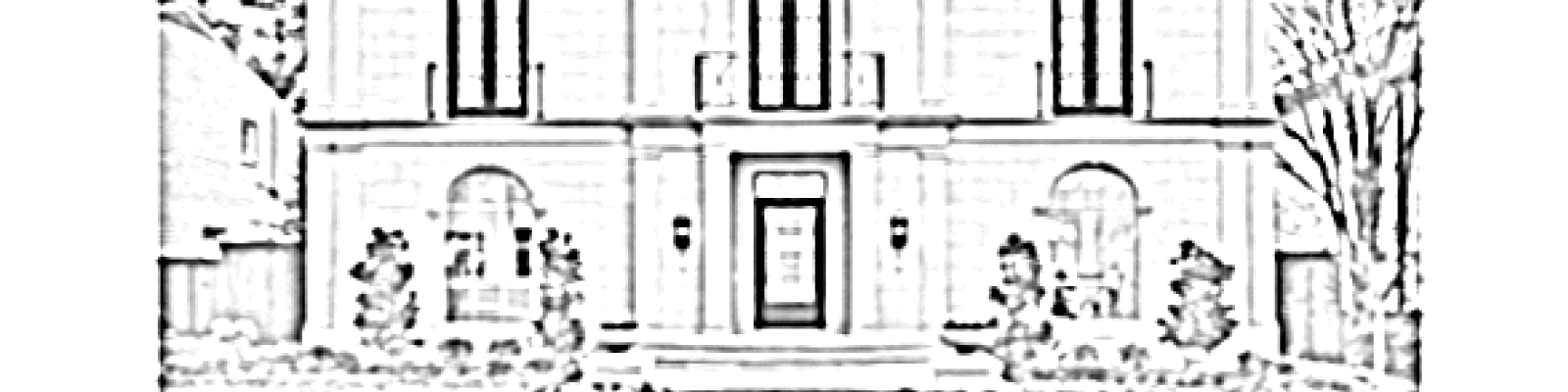

Neo-Classical
Late 18th to early 19th century. Neo-Classical homes are known for their grand scale, simple geometric forms, dramatic front porches with columns, Greek or Roman style detail, and domed or flat roofs. (11)

Prairie
Late 19th to early 20th-century. The style is usually marked by horizontal lines, flat or hipped roofs with broad overhanging eaves, windows grouped in horizontal bands, and disciplined use of ornamentation. (3)

Tudor Revival
1890-1920. Tudor buildings are easily identified by their steeply pitched roofs, often with a front facing gables or multiple gables, and half timbered wall surfaces. (12)
REFERENCES:
(1) Colonial Style | (2) Craftsman Style | (3) Prairie School Style | (4) Dutch Colonial Style | (5) Eastern Brick and Shingle Style | (6) Federal Revival Style | (7) Foursquare Style | (8) French Revival Style | (9) Greek Revival Style | (10) Mid Century Modern Style | (11) Neo-Classical Style | (12) Tudor Revival Style



























